【ベストコレクション】 ”¯Œ^ ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg •”¯ 140793
That fgis di erentiable at every point x2Uand that its derivative is equal to f(x)g0(x)g(x)f0(x) = fDg gDf Note that this derivative is unique by Theorem 912 in Rudin 3 Let T be a linear transformation from Rn to R m Show that T Rn!R is di erentiable as a mapIndian Restaurant SHANTI q X C f B A X g V e B q X C h V eGiven g(x) = 4 – x, evaluate at x = t To evaluate this function at x = t, I'll need to plug t into every instance of x in the formula for the function g g(3) = 4 – (t) = 4 – t There's nothing more I can do with this, and I can't find a fully numerical value because I don't have a number to plug in for the t So my answer is
Chapter 6 Notes
"¯Œ^ ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg •"¯
"¯Œ^ ƒ~ƒfƒBƒAƒ€ ƒXƒgƒŒ[ƒg •"¯-( v"q6 0 0" " b6 &,> 40 , #i£ }"q 6# 0 ro " )"3 Let Ebe an extension eld of a eld Fand f(x), g(x) 2Fx Prove that a greatest common divisor of fand gin Fx is also a greatest common divisor of fand gin Ex 4 Let F be a eld and F its multiplicative group Show that the abelian groups (F;) and (F;) are not isomorphic 5




Let F And G Be Function Continuous In A B And Differentia
Apr 02, 17 · Stack Exchange network consists of 177 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeF(x)=g(x), where f(x);g(x) 2Fx and g(x) 6= 0 However, when we think of F(x) as a eld in its own right, it is traditional to rename the variable xby some other letter such as t,which we still refer too as an \indeterminate," to avoid confusion with xwhich we reserve for the \variable" of a polynomial0g(x)n a 1f(x)g(x)n 1 a nf(x)n = g(x)np(v) = 0 The previous equality implies that f(x) ja 0g(x)n and g(x) ja nf(x)n and hence f(x) ja 0 and g(x) ja n since (f(x);g(x)) = 1 Since a 0 and a n are nonzero this implies that f(x) 2K and g(x) 2K and hence v = f(x)=g(x) 2K Problem 621 Find the degree and a basis for each of the given eld
By Fubini, f(x y)g(y) 2L1(dy) for almost all x, so (f g)(x) is defined for almost all x 2Rn Z jf gj(x)dx = Z Z f(x y)g(y)dy dx Z Z jf(x y)jjg(y)jdy dx = kfk L1kgk L1 Hart Smith Math 526 (f g)(x) = (g f)(x) where the integral exists Proof Letting z = x y, Z f(x y)g(y)dy = Z f(z)g(x z)dz f (g h) = (f g) h Proof Where the d(y;z) integralConst f b a 16a 2 1 x b 2 2 1 x x c x x 2 1 d 2 1 2 x x e 122 xf 242 1 x x g xx from MATH 101 at BMEAnd so jxj sin 1 x h sin 1 x = 2jxj sin h 2x(x h) cos 2x h
SkyArts ́AJava ̃G L X p g W c ̉ Ђł B \ t g E F A AWeb y W ̊J A уR T e B O A Ј Ȃǂ Ă ܂ BMay 29, 13 · The Kolbrin is a series of manuscripts said to have been salvaged from the Glastonbury Abbey fires in 1184 They're said to have a connection with Jesus historically through Joseph of Arimathea, they have been discussed by James McCanney and others View some of the manuscripts online or to buy the book in hard copy It has been rumoured that Nikola Tesla116 = H > B R G B D g Z F b g g h _ h e h ` d b y m g b \ _ j k b l _ l " K \ B \ Z g J b e k d b", L h f 53, K \I 1 1, F _ o Z g b a Z p b y, _ e _ d l j b n



The Graph Of The F X Is Show Below Graph Each Transformed Function And List In Words The Transformation Used Socratic
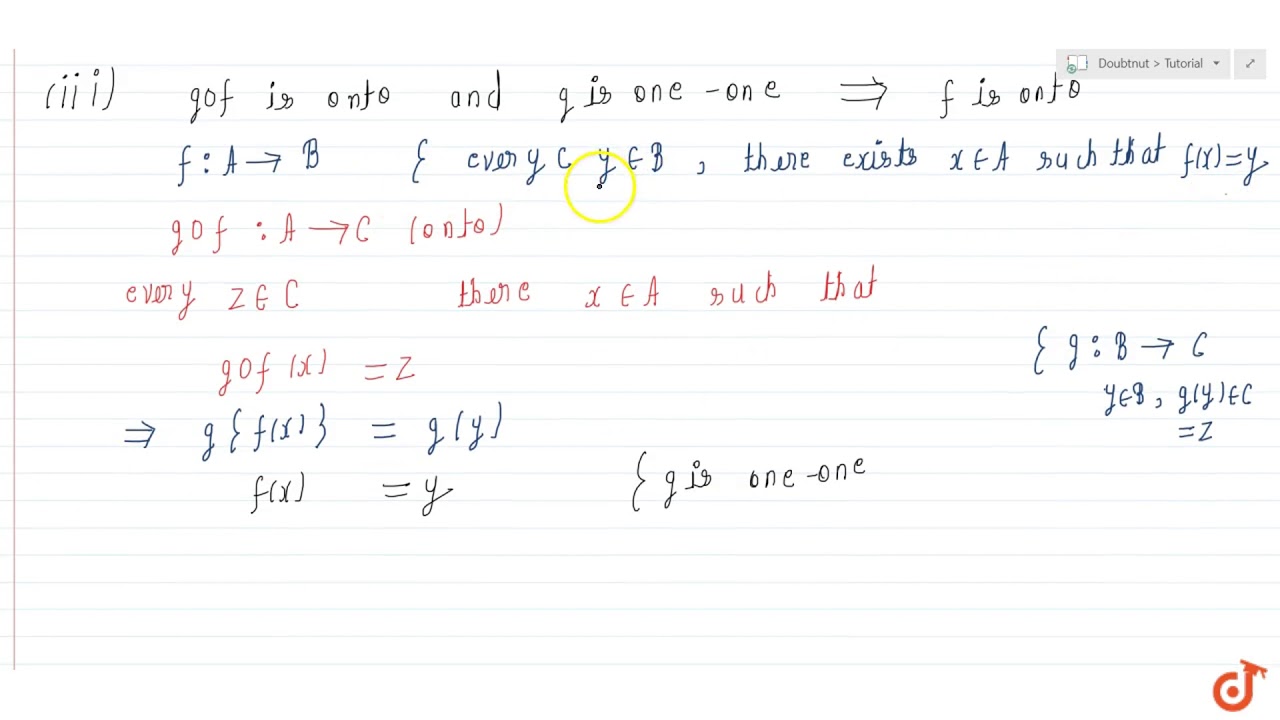



Let F A To B And G B To C Be Two Functions Then I If Gof Is Onto Then G Is Onto Youtube
Rewrite this as a composite function g= 1 x and f= f(x) then g f= f We know gis continuous on every point except 0 and since f(x) k>0 we know gis continuous on the range c;d where f(a;b) ˆc;d Since the composite of a continuous and integrable function is integrable, we nd g fis integrable on a;b which means 1 f is integrable on a;b(a) g is not injective but g f is injective (b) f is not surjective but g f is surjective Solution The same example works for both Let A = f1g, B = f1;2g, C = f1g, and f A !B by f(1) = 1 and g B !C by g(1) = g(2) = 1 Then g f A !C is de ned by (g f)(1) = 1 This map is a bijection from A = f1gto C = f1g, so is injective and surjectiveJ b g o X ԃX y X ͍ő 11 䕪 p ӂ Ă ܂ B( ɂ 蒓 ԃX y X Ȃ Ȃ ꍇ ܂ B ڂ ͂ ₢ 킹 B)




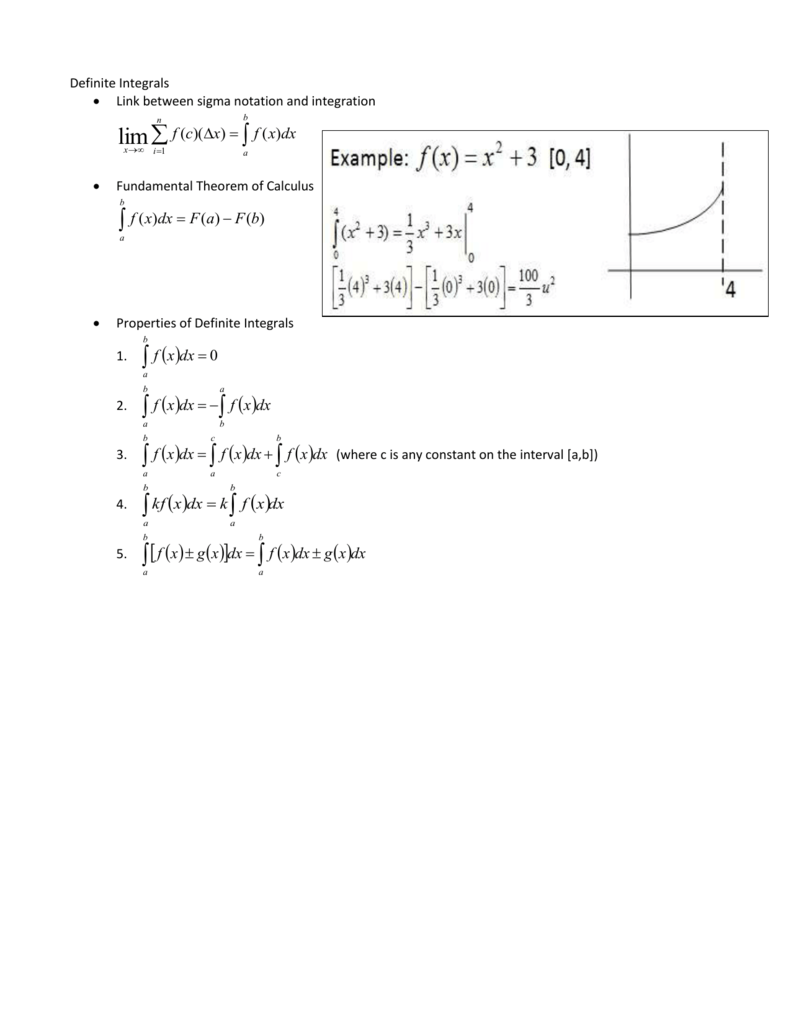
Definite Integrals Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange



Ap Calculus Ab Multiple Choice 1998 Exam Part B Videos Questions Solutions
F B A X g @ e r ԑg @ u m ؉x q v i ̃h } Ȃ @ W I ԑg @ u m ؉x q v i ̃ W I h } @ f @ u m ؉x q v i ̉f 扻 @ 䉻 i @ u m ؉x q v i ̕ 䉻 @ r f I E c u c Ȃ @ h } E f ̃r f I ȂA X ^ E x f B A X g R E N A ` A E v g B b ` F u ΌQ v ɂā012 N04 30 B e B(photo by Aya Suehiro) Shu Suehiro shu@botanicjpBut then G(x) = g(x) on (0;1), and so g(x) is also uniformly continuous Failed attempt at a solution ( x h)sin 1 x h sin 1 x sin j j 1 x h 1 x 1 x h jxj sin 1 x h sin 1 x jhj For the rst term, we use the fact that sinA sinB= 2sin A B 2 cos A B 2 ;




Example 19 Show That If F G Are Onto Then Gof Is Also Onto




If F Is Continuous On A B And Int A B Fg 0 For Any G Defined On A B Then F X 0 Forall X In A B Mathematics Stack Exchange
@ ܂˂ N u @ K f B A ܍ i X g Guardian Children's Fiction Prize ( Guardian Award for Children's Fiction) ŏI X V @ @ @16 N O X g ljF B A V X g s J d b ł̂ \ E ₢ 킹 TEL s V h s J 25 ԒnЊT v ̃y W B Ńz y W 삵 Ă X } g f B A ł B B ͖ q f U C N T A ƂƂ q l ֏Ί ł 悤 ɁA l X ȉ \ ͍ Ă ܂




Misc 15 Let F X X2 X G X 2 X 1 2 1 Are F G




Section 1 5 Combinations Of Functions Ppt Download
Therefore, f (x) = g (x) C f (x) = g (x) C for all x ∈ I x ∈ I The third corollary of the Mean Value Theorem discusses when a function is increasing and when it is decreasing Recall that a function f f is increasing over I I if f ( x 1 ) < f ( x 2 ) f ( x 1 ) < f ( x 2 ) whenever x 1 < x 2 , x 1 < x 2 , whereas f f is decreasing over5 Let f (x) = g(x)h(x) be a product of two irreducible polynomials over a finite field Fq Let m be the degree of g(x) and n be the degree of h(x) Show that the degree of the splitting field of f (x) over Fq is equal to the least common multiple of m and n Solution Fqm is the splitting field for g(x), Fqn is the splitting field for h(xChapter 8 Integrable Functions 81 Definition of the Integral If f is a monotonic function from an interval a,b to R≥0, then we have shown that for every sequence {Pn} of partitions on a,b such that {µ(Pn)} → 0, and every sequence {Sn} such that for all n ∈ Z Sn is a sample for Pn, we have {X (f,Pn,Sn)} → Abaf 81 Definition (Integral) Let f be a bounded function from an interval




Solved If F And G Are Continuous On A B Then So F X G Chegg Com



Functions F G And H Are Twice Differentiable Fu Gauthmath
4 Patience, the Key / Come Here, Baby 5 Sh Listen 6 Forever My Sweet 7 Gotta Get Down ft Choklate 8 G is for Grüv / Areola 9 U R Me 10 Glorious Trip 11 Again, the Key / Pretty Girl Makin' Me Smile On Tu Me Manques, Sax G explores lonely worlds, weaving melancholyK f B A ܍ i X g ł B 1980 N @ K f B A ܍ i @Guardian Award for Children's Fiction ܔN MS A X G Tu Me Manques, released 12 March 13 1 Sax's Heartbeat 2 Tu Me Manques ft Choklate 3 Now What?




Writing Exponential Functions From Tables Algebra Video Khan Academy




Ax B And G X Cx
C ^ l b g ƃ} ` f B A Ɋւ I C ̎ T l p ԂɌ t Ċy ރN X h E p Y ̂ ƂŁA C X G ŌR p ʐM ̈Í Z p Ƃ ĊJ ꂽ ׂ ƍ ̎l p ̑g ݍ 킹 łł 2 o R h E V X e ̖ ̂ɂȂ Ă ܂ BCan you express `d` in terms of `g` and `c`?O ȃX g E F V A ̏ Ώ ŁA w Stranvaesia davidiana B p Chinese stranvaesia B Chinese stranvaesia belongs to Rosaceae (Rose family) It is an evergreen shrub that is native to western China This shrub can reach about 18 m in



Solved True Or False Explain Your Reasoning If F And G Are Continuous On A B Then A B F X G X Dx A B F X Dx Course Hero
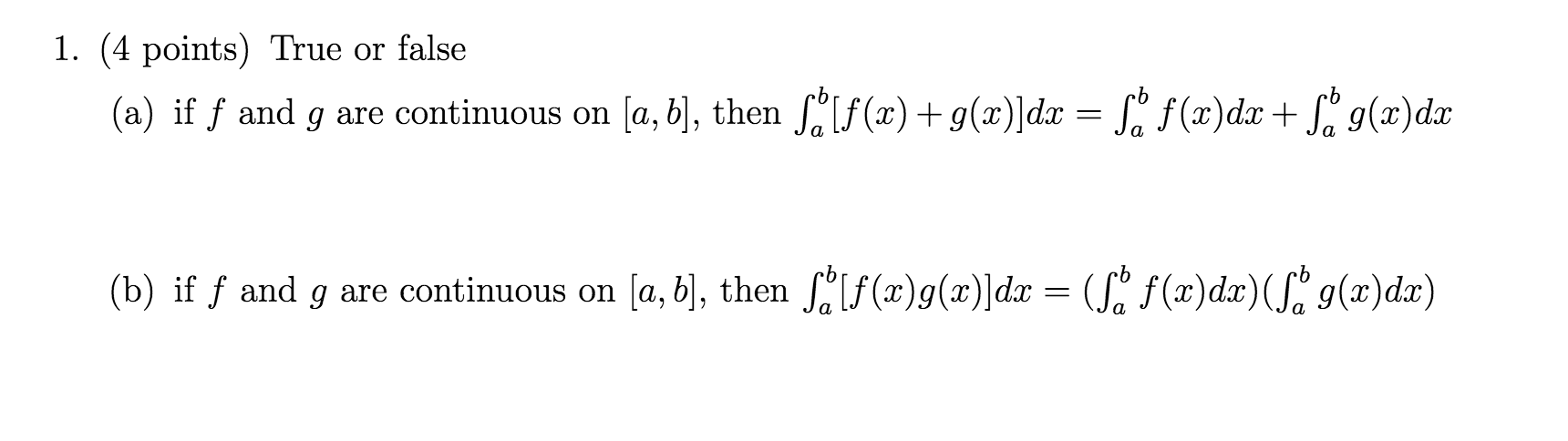



Solved True Or False If F And G Are Continuous On A B Chegg Com
Let G(x) be any function withthe property that G · (x) = f(x) Then ∫b a f(x)dx = G(b) G(a) ProofAsabove, we introduce the area function F(x) = ∫ x a f(t)dt (2) By the firstfundamental theorem, F · (x) = f(x) Since F(x) and G(x) have the same derivative, they must differ by a constant (Corollary 427 onpage 294) 4{ f R A e B X g ́A f R A g ̕ y Ɛ Z p ̔ W A ړI Ƃ A f R A g Ɋ֘A Ƃ𒆐S Ƃ Đݗ ꂽ c ̂ł B u f R A e B X g v Ƃ́A f R d E f R O b Y ɑ \ 郉 C X g Ȃǂ g p f R V Z @ g f R A g h ̐ Z p ҂ w ܂ BC ^ l b g ƃ} ` f B A Ɋւ I C ̎ T CATV U iTV(interactive TeleVision) č ̃u h o h ƃ_ C A b v ɂ ƒ ̈Ⴂ




Answered 149 3 2 The Derivative As A Function Bartleby
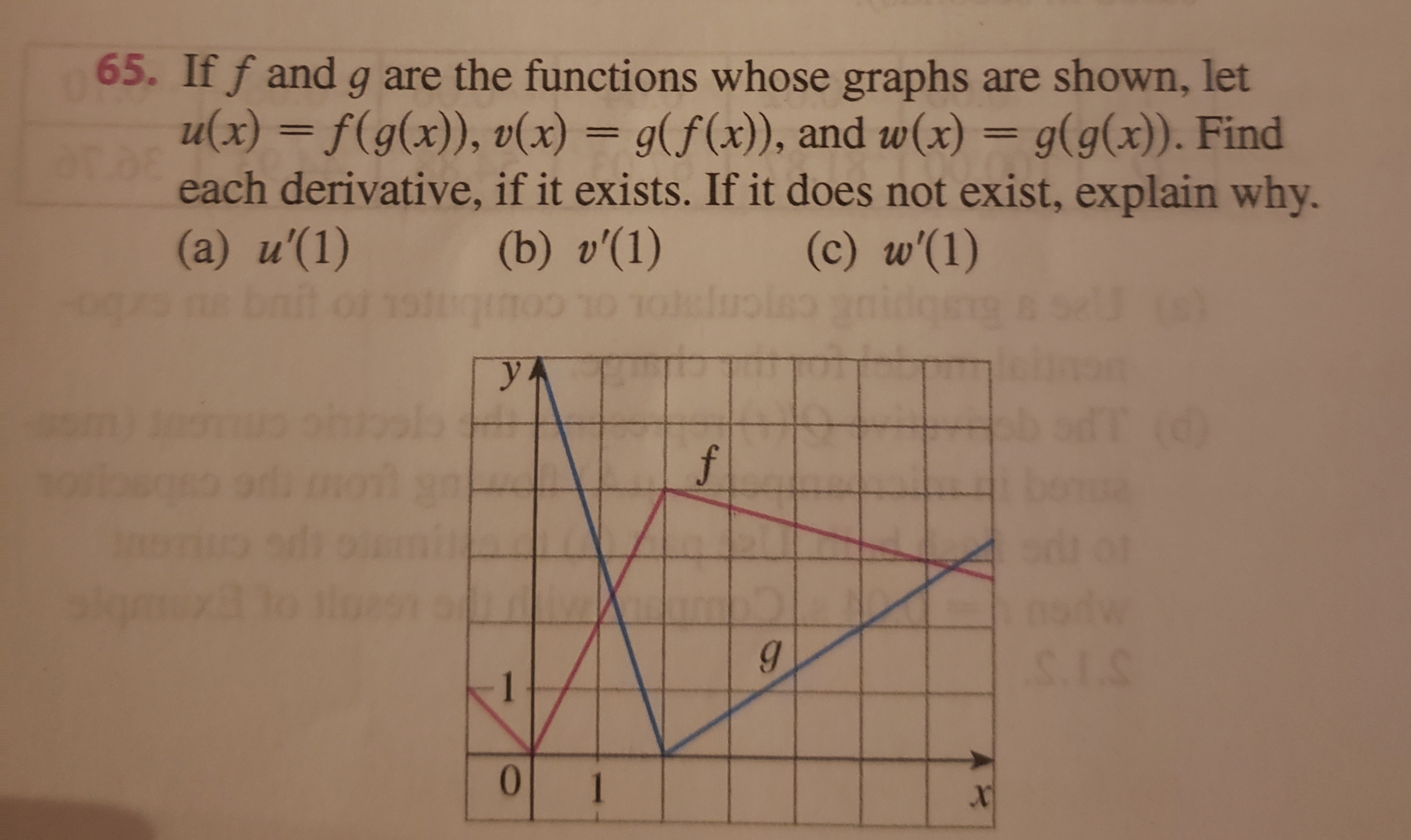



Answered 65 If F And G Are The Functions Whose Bartleby
Use the links on this page to get the information you need about Windows Media Player and other Windows Media technologies Windows Media PlayerC ^ l b g ƃ} ` f B A Ɋւ I C ̎ T The Daily Telegraph 04 N5 4 ɕ A C M X ƕĕ ɂ C N l ߗ s ҂̎ʐ^ Ɛ E ̃ f B AWe are given `f` and `g` and our goal is to compute `g'(c)` Just by looking at the graphs, what tells you that `f` and `g` are inverses?




2 4 Solving Equations And Inequalities By Graphing Mathematics Libretexts




Calculus Practicals Maxima And Minima Derivative
)µ m 0 r #if "q (2 ( !"mtb ! # ;q¹ m !" % 5 £ (" "q0' 0 £"q0 r5 , yd p 6 % ?Dr Guozhong Cao is the BoeingSteiner Professor of Materials Science and Engineering and Adjunct Professor of Chemical and Mechanical Engineering at the University of Washington He received his PhD from Eindhoven University of Technology (the Netherlands) Dr Cao has published over 0 refereed papers, and authored and edited 4 books and 3Type Notes Uploaded By Ashleyshalima Pages 58 This preview shows page 24 28 out of 58 pages




If F X X G X X X Then Which Of The Following Functions Is
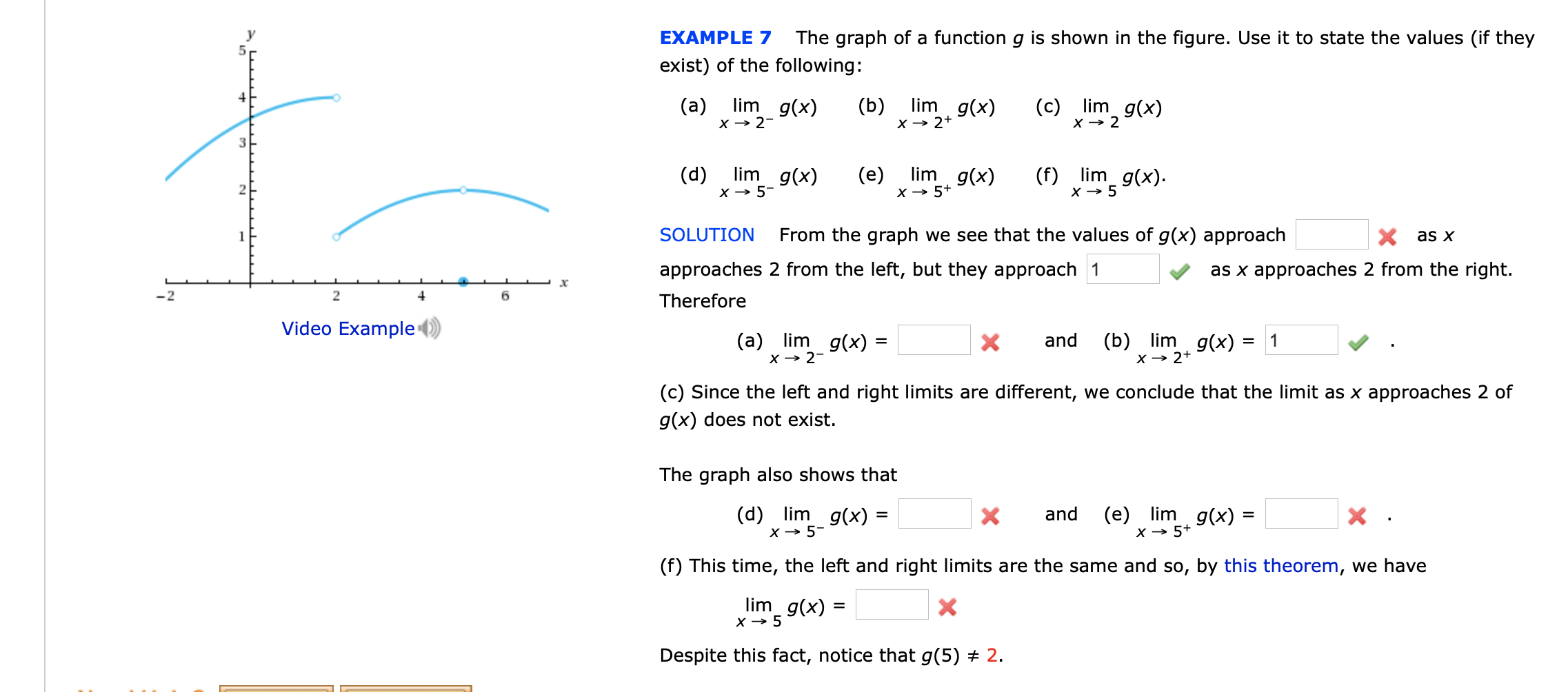



Answered The Graph Of A Function G Is Shown In Bartleby
7 Let f A → B and g B → C Prove that if g f is onetoone then f must be onetoone PROOF ASSUME g f is onetoone, ie, (∀a,b ∈ A) g f(a) = g f(b) ⇒ a = b Show that f is onetoone Let a,b ∈ A f(a) = f(b) ⇒ g(f(a)) = g(f(b)), since g is a function ⇒ g f(a) = g f(b), by definition of g f2 (a) Define uniform continuity on R for a function f R → R (b) Suppose that f,g R → R are uniformly continuous on R (i) Prove that f g is uniformly continuous on R (ii) Give an example to show that fg need not be uniformly continuous on R Solution • (a) A function f R → R is uniformly continuous if for every ϵ > 0 there exists δ > 0 such that f(x)−f(y) < ϵ for all xCourse Title MATHEMATIC 101;
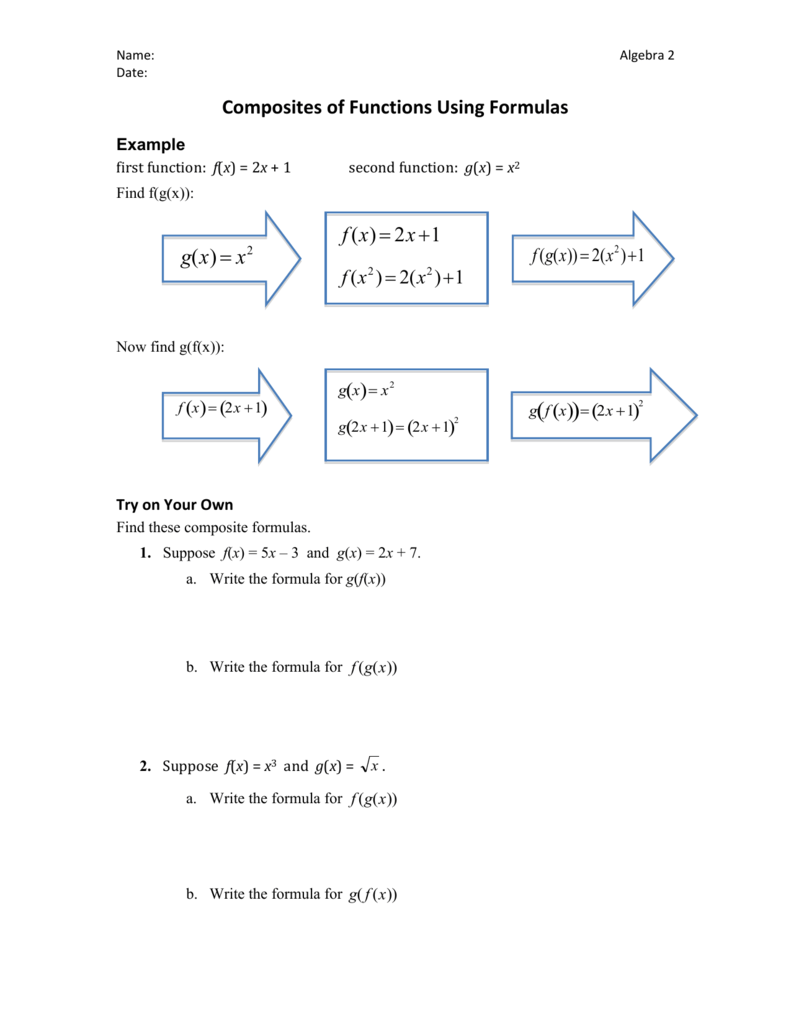



Composite Functions Formulas Homework Problems



Solved Mathboat Com 4 Nc The Function F X And G X Are Piecewise Linear Functions Shown Below If H X F G X G X Then Hil 4 0 Course Hero
GivengRn 1mthe Frechet derivative ofg at apoint x ERn,if it exists, is the linear mappingg'(x) RnR'(if it exists, it is unique) for which g(y) g(x)4g'(x)(y x) o(lly xll), where limo(llyxll) IIxll Since gl(x) is a linear mapping fromn tom, it has a matrix representation in mn,withrespect to the standard basis ThisMATH 6102 — SPRING 07 ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS February 12, 07 1 Let f be integrable on a,b, and suppose that g is a function on a,b so that f(x) = g(x)Prove that if f and g are Riemann integrable on a,b (ie f,g 2 Ra,b) and there exists N ¨0 such that g(x) ‚1/N for all x 2a,b, then f /g 2Ra,b Solution Let g be bounded above by M on a,b By Theorem 611, since `(x) ˘ 1 x is continuous on 1 N,M (because it doesn't contain 0), then `(g(x)) ˘ 1 g(x) is Riemann integrable on



Calculus Index Cards




Chapter 6 Notes
Feb 26, 18 · Mathematics Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for people studying math at any level and professionals in related fields It only takes a minute to sign up͍ς݃f ^ @ @ @ p y W R h ̓ e ́A y W 炨 肢 ܂ B } X ^ R h @ K { ECC 142E7218 1CA CMath 432 Real Analysis II Solutions to Homework due March 11 Question 1 Let f(x) = k be a constant function for k 2R 1 Show that f is integrable over any a;b by using Cauchy's " P condition for integrability
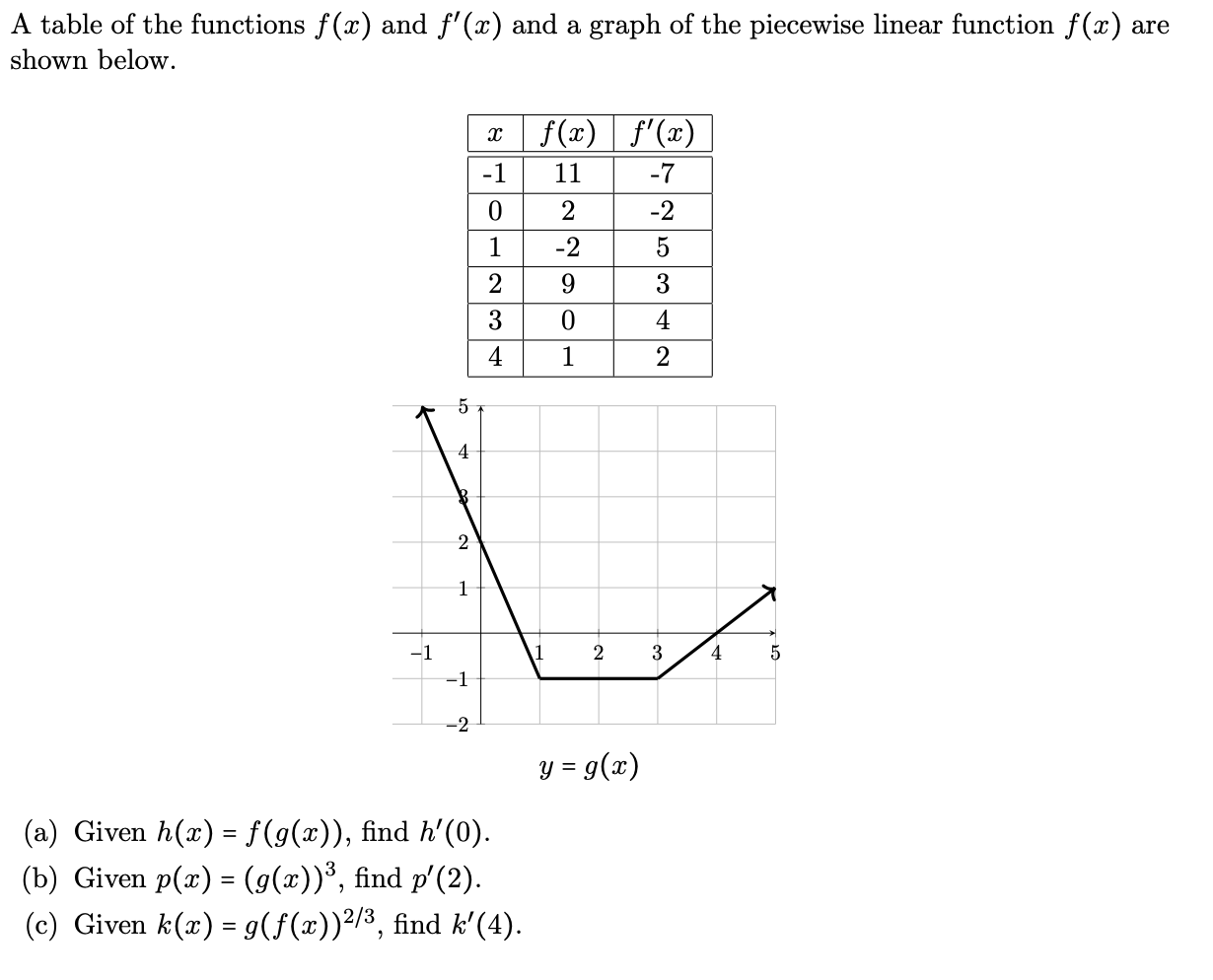



Solved A Table Of The Functions F X And F X And A Grap Chegg Com




Answered Express The Function In The Form F G 1 Bartleby
Step 1 Justify if point `(c, d)` lies on the graph of `g`, then the point `(d, c)` lies on the graph ofB a b a b a dx x f b a x f dx x g dx x f b a x g x f Average Mean Value If f is B a b a b a dx x f b a x f dx x g dx x f b a x g x f School Moi University;Harry Allen Meets John Pizzarelli Trio @ 1996BMG VictorJapan Album Title @ @ @ @ @ @ f B A E I h E X g b N z




Let F And G Be Function Continuous In A B And Differentia
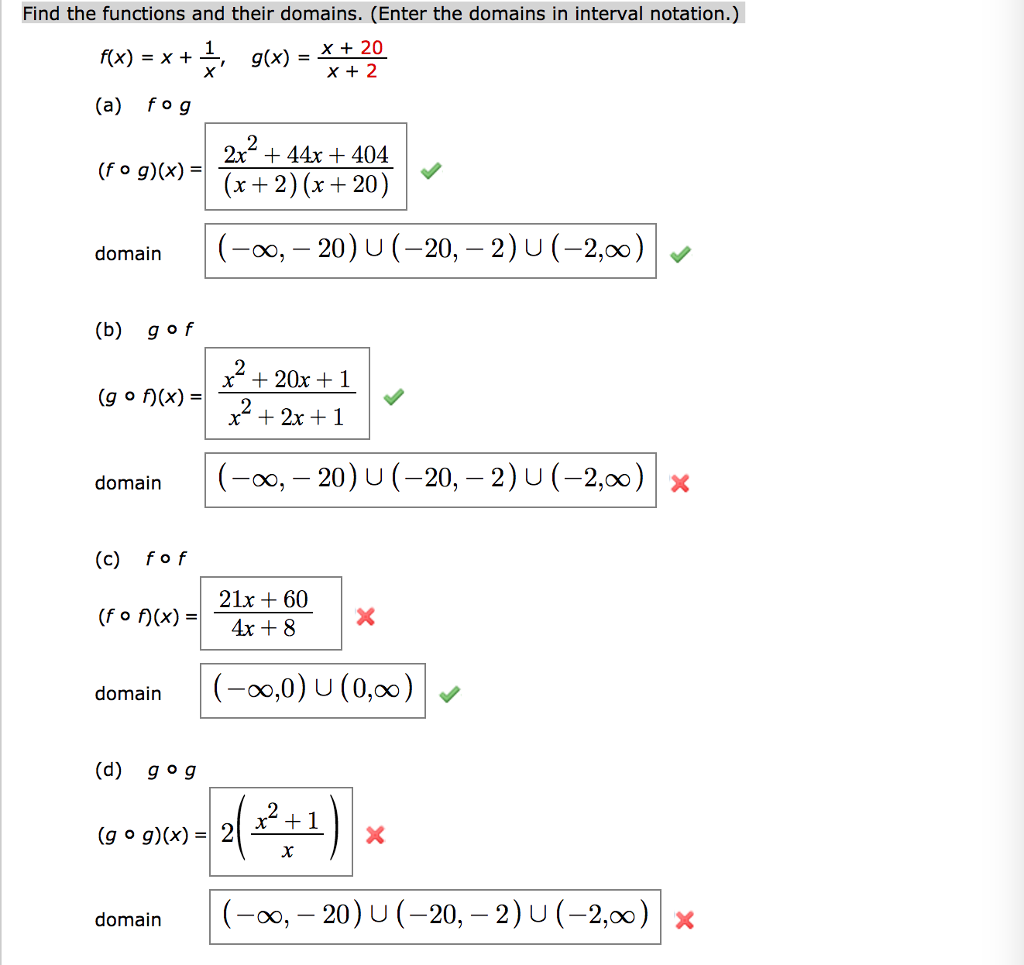



Solved Find The Functions And Their Domains Enter The D Chegg Com
Proof Let F = f − g, then F' = f' − g' = 0 on the interval (a, b), so the above theorem 1 tells that F = f − g is a constant c or f = g c Theorem 3 If F is an antiderivative of f on an interval I , then the most general antiderivative of f on I is F(x) c where c is an constant




Notes On Topics Of Algebra Notes




How To Find Out That The Set Of Points At Which Two Continuous Functions Are Equal Is Open Or Not Mathematics Stack Exchange



Composite Functions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions




Which Comparison Is Correct For The Values Of F X And G X When X 1 Function A F X Brainly Com




2 4 Solving Equations And Inequalities By Graphing Mathematics Libretexts




Let F And G Be Differentiable Functions Such That Xg F X F G X G X F G X G F X F Youtube
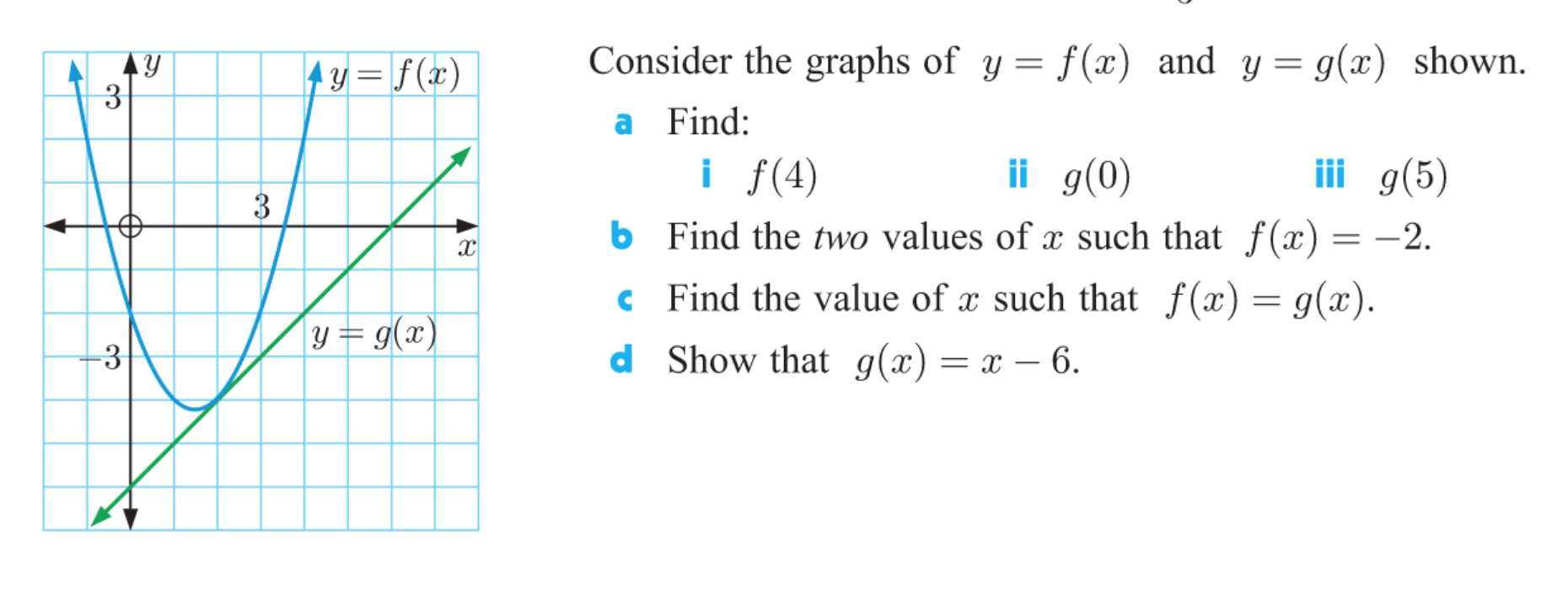



Answered Consider The Graphs Of Y F X And Y Bartleby




Answered G B Use The Substitution Bartleby




Which Comparison Is Correct For The Values Of F X And G X When X 2 Function A F X 3 X 2 Brainly Com



Solved If F And G Are The Functions Whose Graphs Are Shown Let U X F G X V X G F X And W X G G X Find Each Derivative If It Exi Course Hero



Writing Exponential Functions From Graphs Algebra Video Khan Academy
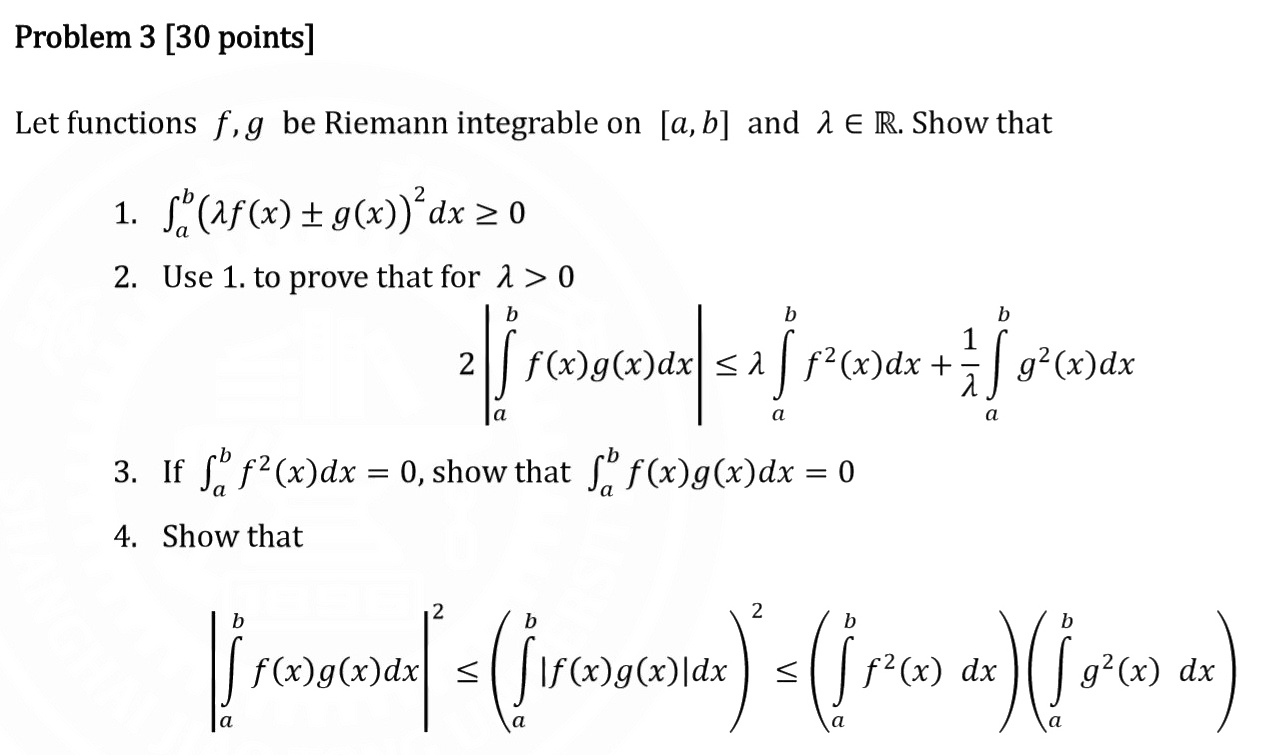



Solved Let Functions 𝑓 𝑔 Be Riemann Integrable On 𝑎 𝑏 Chegg Com




F X X2 What Is G X G X 5 1 4 F X ܕ 5 O A G X 1x2 B G X 4x O C G X 4x O Brainly Com
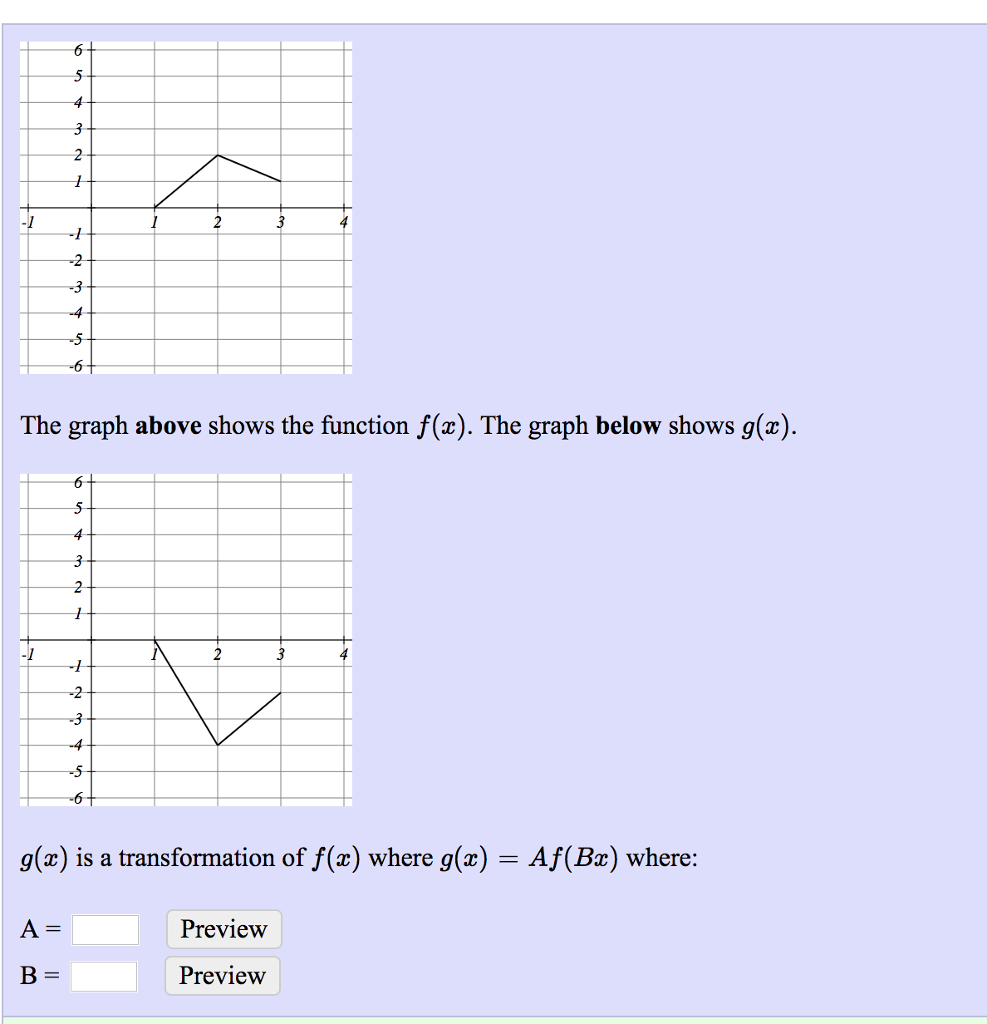



Solved The Graph Above Shows The Function F X The Graph Chegg Com
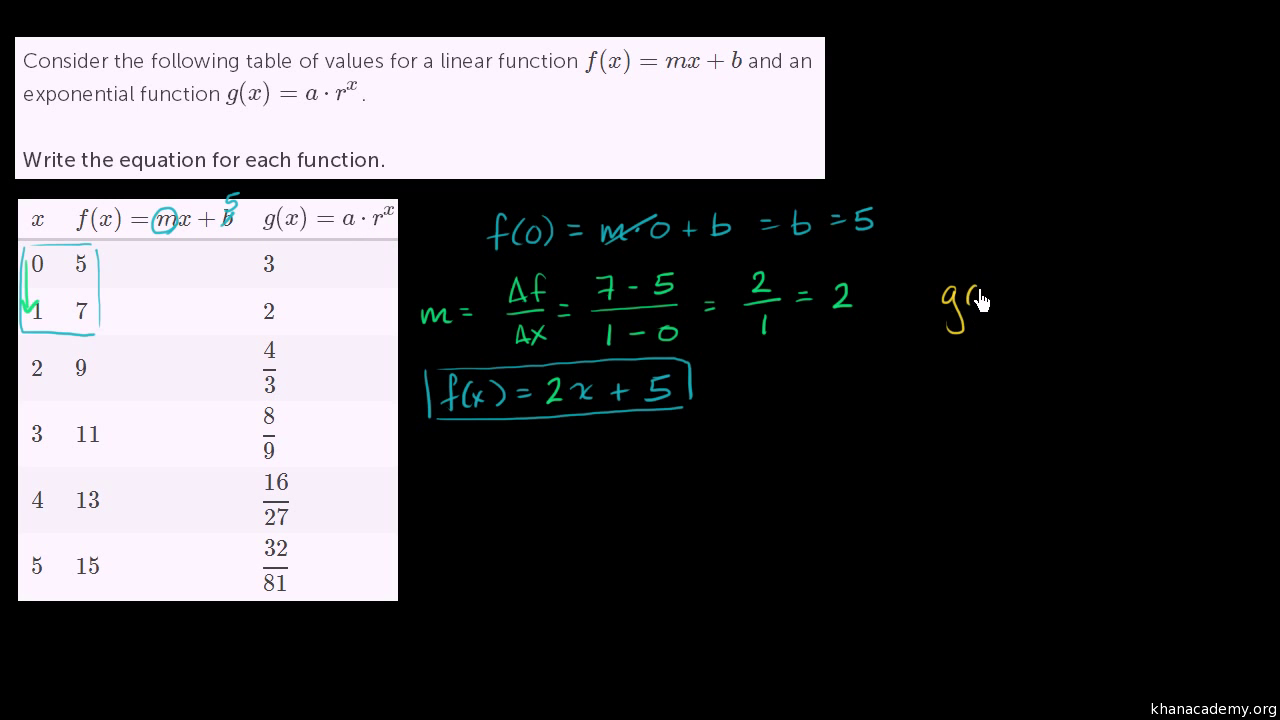



Writing Exponential Functions From Tables Algebra Video Khan Academy




Help Needed With Calculus Question Wyzant Ask An Expert




Use The Graph That Shows The Solution F X G X F X X 2 4x 2 G X 1 2 2 1 What Is The Brainly Com
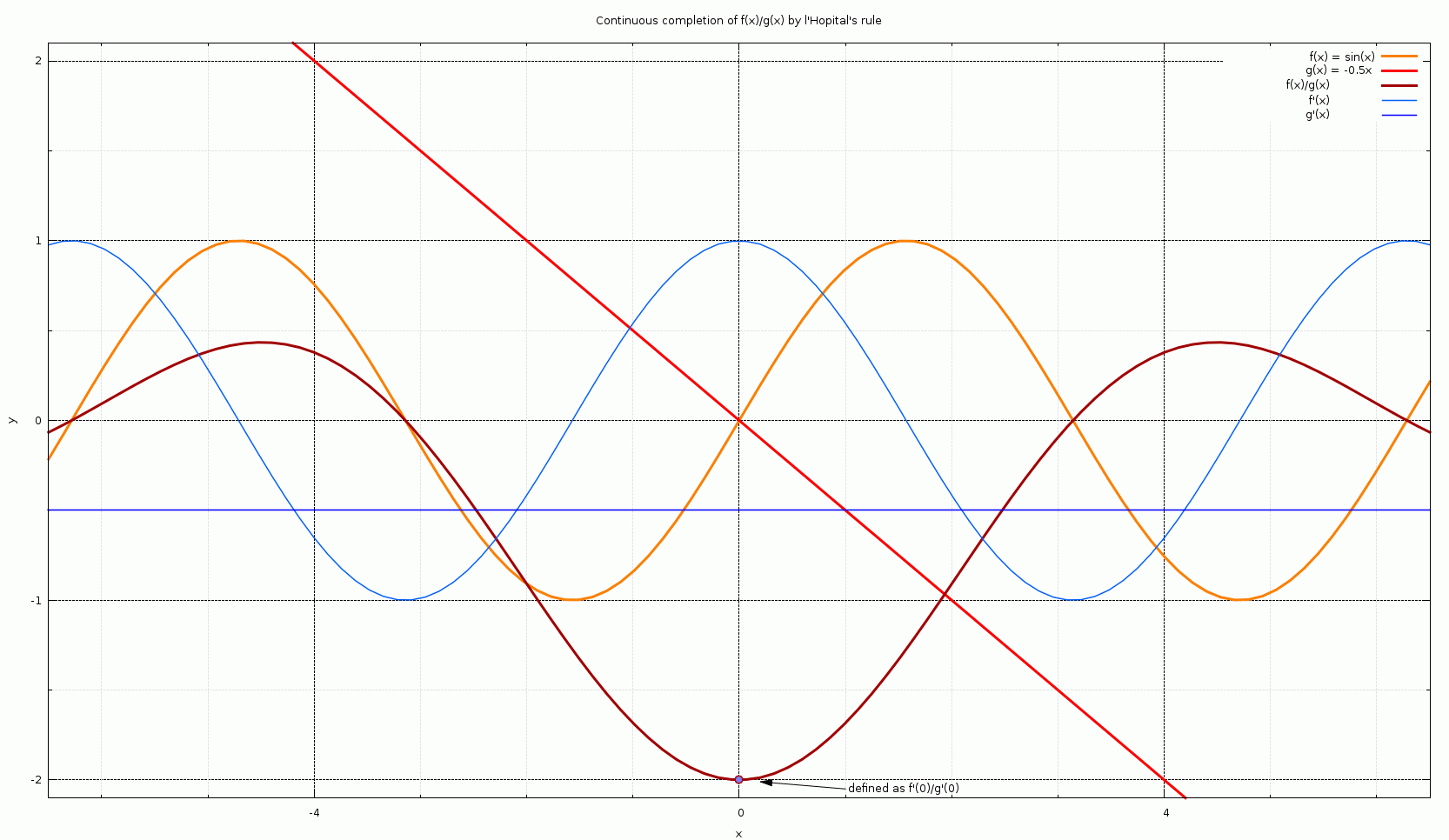



L Hopital S Rule Wikipedia




Function Mathematics Wikipedia
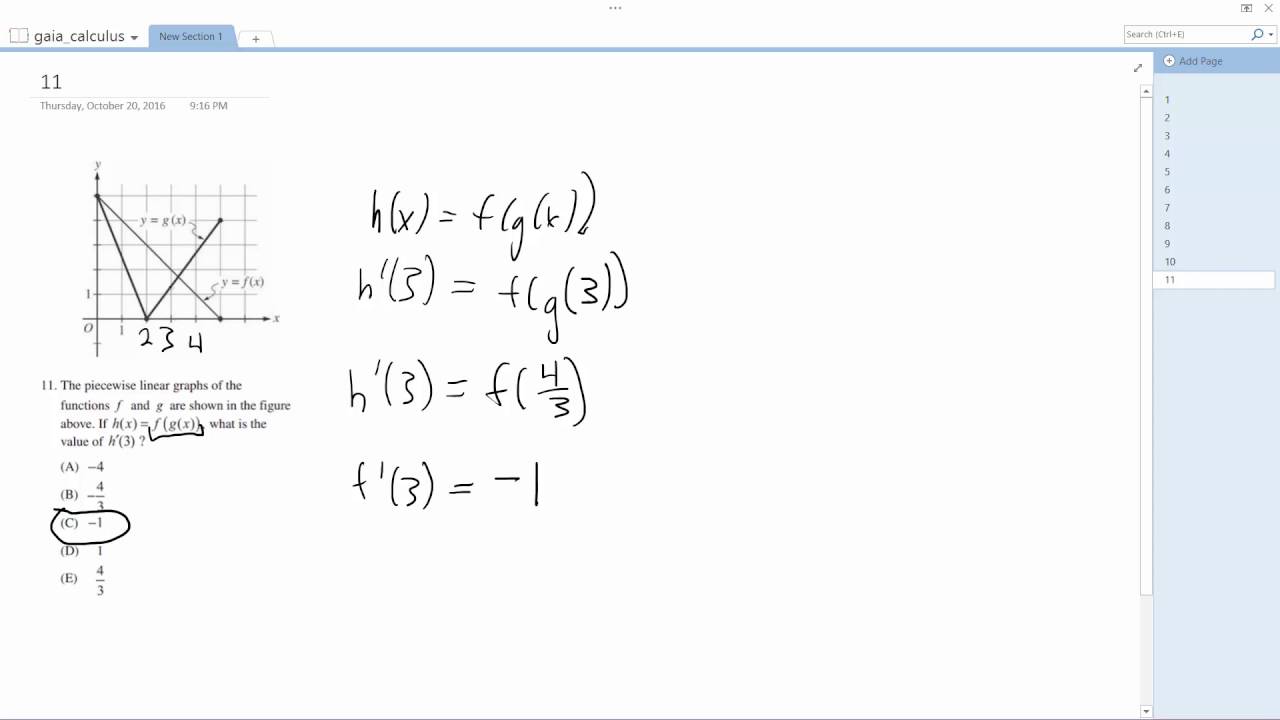



If H X F G X What Is The Value Of H 3 Youtube




Solved 1 Given The Functions F X X 1 And G X 3 Chegg Com



Calculus Index Cards
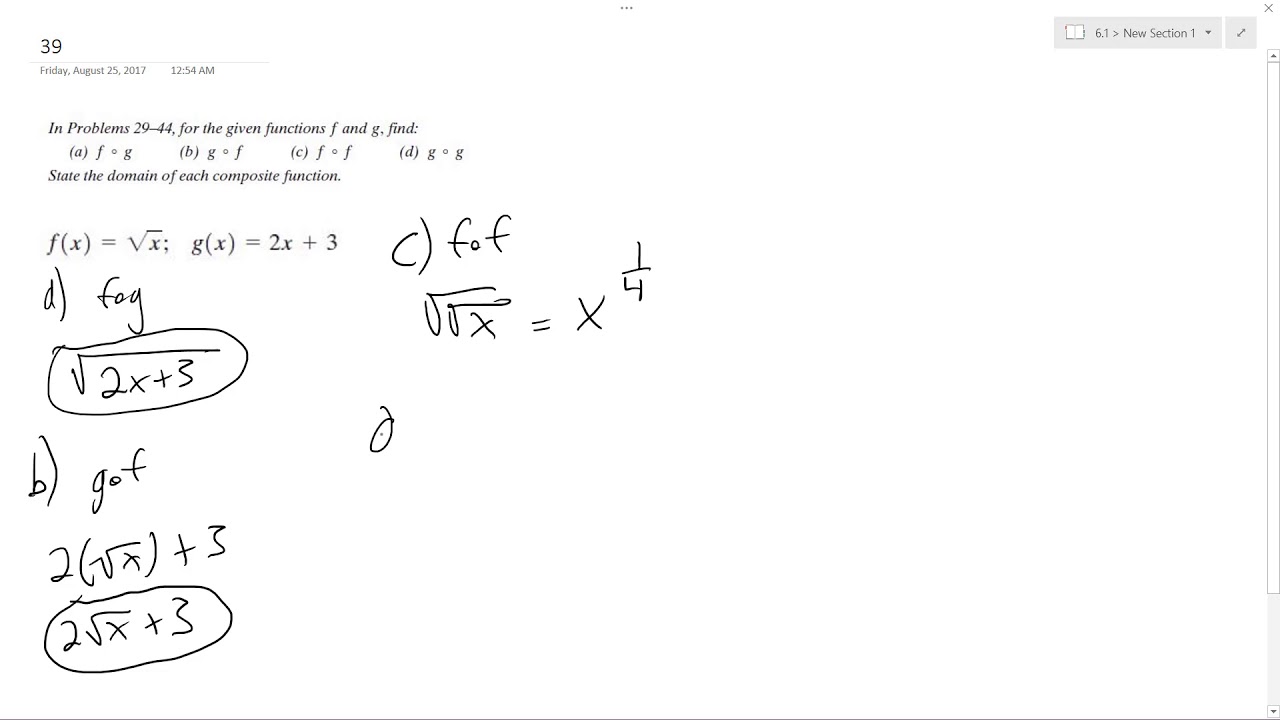



F X Sqrt X G X 2x 3 Youtube
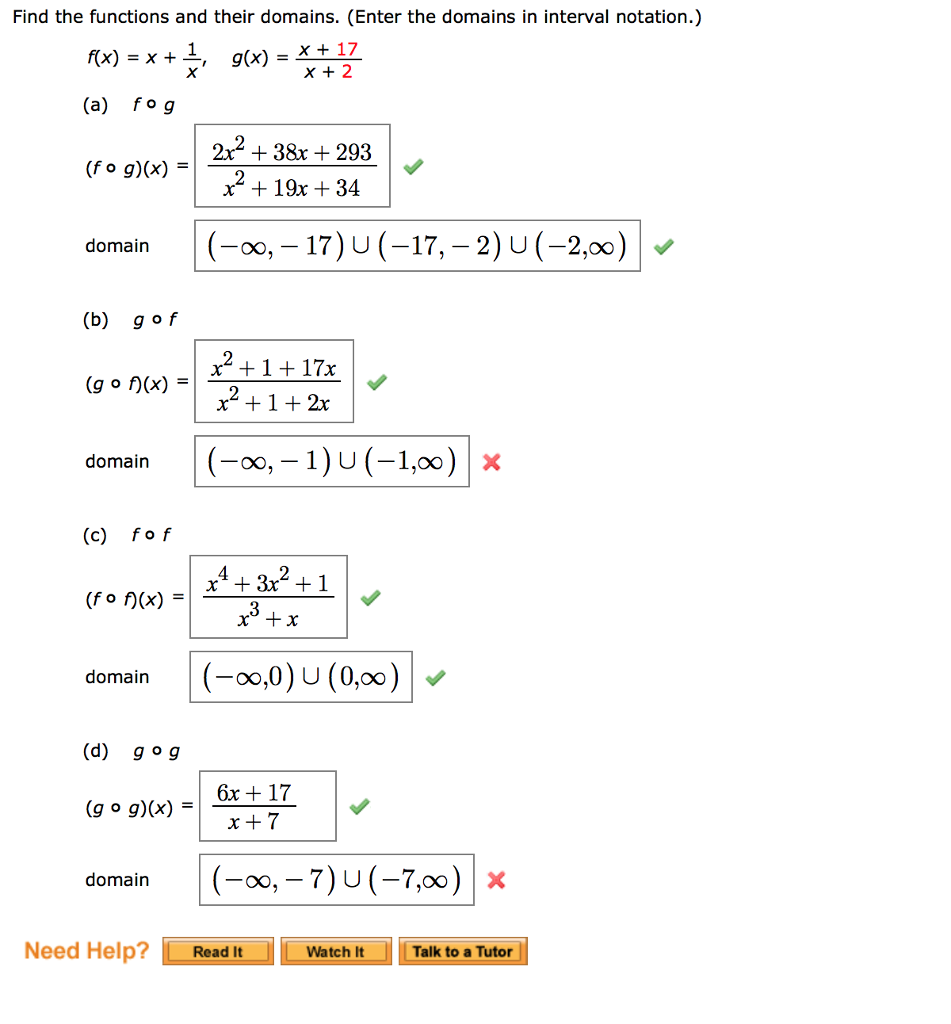



Solved Find The Functions And Their Domains Enter The Do Chegg Com




Stem Engine General Mathematics Operation On Functions Facebook




Algebra And Composition Of Functions Ppt Download




Functions Composite Ppt Download
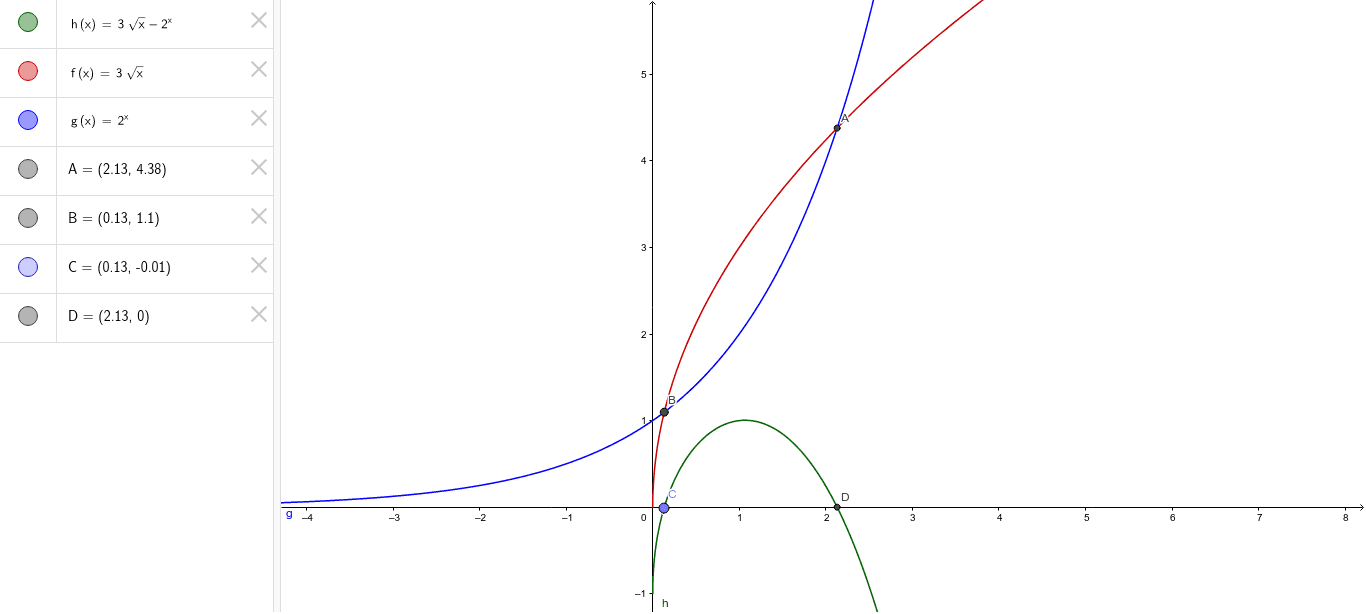



Graph Of F X G X F G X Geogebra




Definitions For A Function F A B The Inverse Of F Is The Following Relation From B To A F 1 X Y Y X F For Functions




If F X And G X Are Two Functions With G X X 1 X And F G X




Spm Add Maths Page 54 User S Blog




2 4 Solving Equations And Inequalities By Graphing Mathematics Libretexts
コメント
コメントを投稿